Expert Insight: Understanding the Diesel Emission System
The Diesel Emission System (DES) is a set of components working in concert to reduce harmful pollutants emitted from diesel engines into the atmosphere. When diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining these components, it is essential that you look at the entire system.
This article will explain the different components that make up the Diesel Emission System and highlight how they must be treated as one complete system.
We will cover the following:
- One Box vs Standard Diesel Emissions System (DES)
- Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOC)
- Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
Understanding how these components work together as a system will help you to make parts recommendations to repair technicians who are diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining diesel emissions systems.
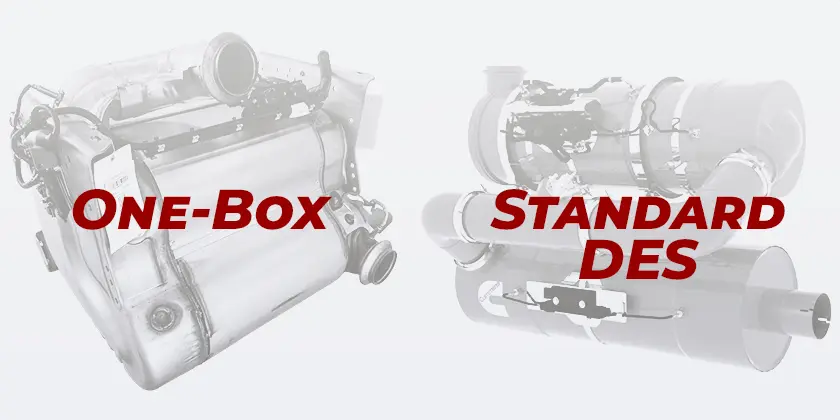
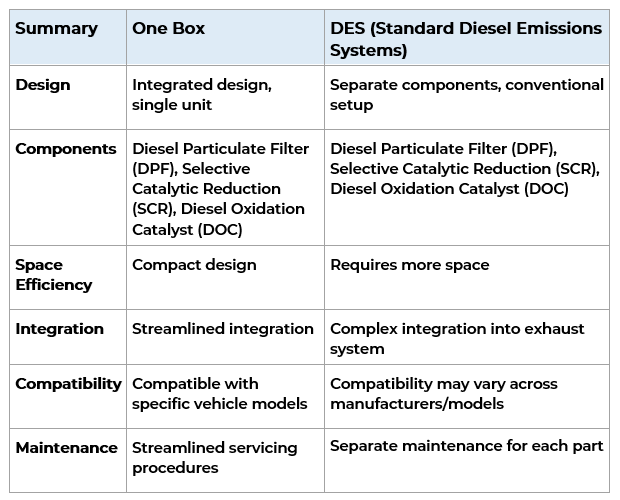
One Box vs Standard Diesel Emissions System (DES)
The One Box System
The One Box is an emissions control system developed by Freightliner, a leading manufacturer of commercial vehicles. It’s designed to streamline emissions control in heavy-duty trucks by integrating multiple components into a single unit.
The One Box setup is specifically engineered to be compatible with Freightliner (and related) truck models, ensuring seamless integration and enhanced reliability. Not all One Box systems are the same as different versions have been made over time to meet different rules, regulations, and mounting configurations.
When ordering parts, it is important to know which One Box model is being worked on by getting the part number from the unit’s label.
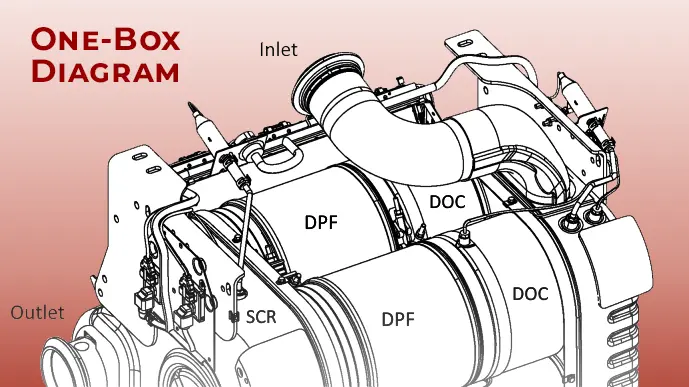
The One Box system typically includes components such as diesel oxidation catalysts (DOC), diesel particulate filters (DPF), and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems, all housed within a compact and efficient package. See the diagram and video to learn more about the One Box system.
However, unlike other emission systems, the One Box does not allow you to remove and clean the DOCs and SCRs since these are built into the unit for space efficiency. Only the DPFs are removable for cleaning.
There are several methods of cleaning the entire One Box unit, but mostly it involves baking the entire unit in an oven and then blowing out any resulting ashes.
The Diesel Emission System (DES)
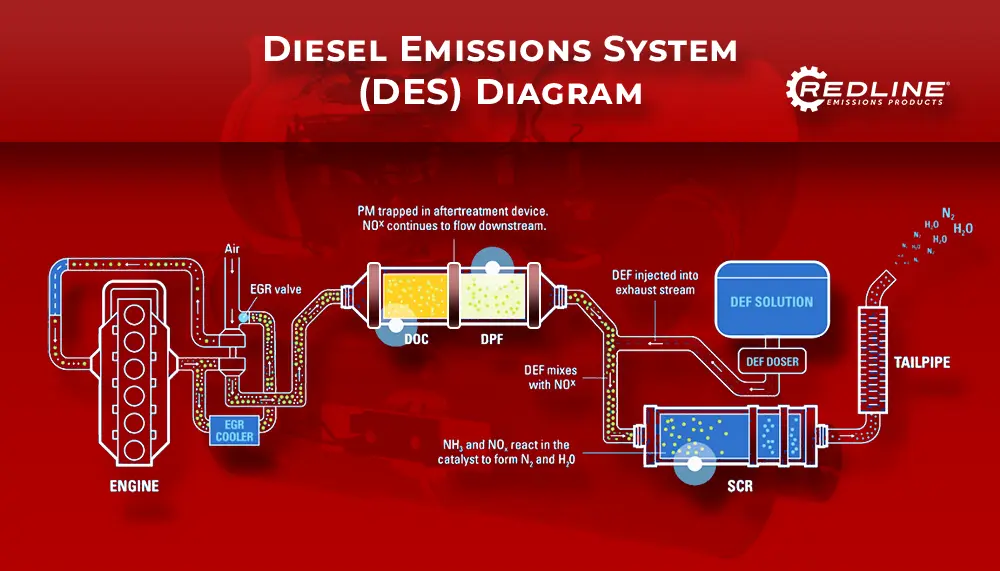
The standard Diesel Emission System (DES) is used in heavy-duty trucks to control emissions, and it is made up of separate components such as diesel oxidation catalysts (DOC), diesel particulate filters (DPF), and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems. Each component plays a specific role in reducing emissions from the exhaust gases produced by the engine.
The process begins with the diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC), with its catalytic coating, elevating exhaust gas temperature to reduce carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HCs). Then, the diesel particulate filter (DPF) captures and stores emitted debris until regeneration conditions are optimal. The clean exhaust gas then undergoes diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) treatment before entering the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) to eliminate any remaining nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions.
The standard DES generally requires more space on the diesel vehicle/truck than the One Box design but offers greater compatibility across manufacturers. Maintenance and servicing for DES components are typically performed separately, making it somewhat less complex to maintain.

What is the Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC)?
The Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) is an aftertreatment device installed in the diesel emission system to reduce harmful pollutants in the exhaust stream before they are released into the atmosphere. They achieve this through a catalytic process.
The DOC substrate has a ceramic coating with precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium serving as active sites for chemical reactions. As hot exhaust gases flow through the DOC, they encounter the catalyst and the metals promote the conversion of primarily carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HCs), transforming them into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). This process significantly reduces the harmful substances released into the environment. DOCs contribute to improved DPF regeneration by removing some particulate matter (PM) and conditioning the exhaust gases. There should be a temperature increase across the DOC to assist the DPF in oxidating the PM stored.

What is a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)?
The Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) is an aftertreatment device designed to reduce diesel soot particulate matter (PM) emissions from the exhaust stream before it is released into the atmosphere. They achieve a PM reduction rate of 85% to 100%. However, the accumulated particles need to be converted into ash to keep the filter’s effectiveness.
This process, called regeneration, can occur in two ways:
Passive Regeneration
Occurs naturally during regular highway driving conditions when the exhaust temperatures naturally rise to a level sufficient to burn off trapped soot particles. The soot is oxidized leaving ash.
Active Regeneration
Requires an intentional increase in the exhaust temperatures to a level suitable for regeneration. This is necessary when normal driving conditions do not generate enough heat to burn off soot trapped in the diesel particulate filter (DPF). This involves injecting a small amount of diesel fuel or a catalyst into the exhaust stream upstream of the diesel particulate filter (DPF), which raises the temperature within the DPF to allow for the combustion of trapped soot particles.
Over time, if the DPF is ignored, the ash in the channels can react with moisture and turn into a cement-like material, a process called sintering. Sintering will build up in the DPF, not allowing air to pass through, reducing volumetric efficiency, and increasing back pressure. In many cases, sintering cannot be removed from a DPF.
Additionally, the DPF employs wall flow filters, featuring alternating plugged channels on the inlet side. If the inlet side is plugged, the outlet side will be open, and vice versa. Exhaust gasses enter the open channel and encounter the plug, forcing the gasses through the wall of the channel to an adjacent one with an open outlet, leaving the PM behind. During regeneration, the collected PM is converted to ash and will remain in the DPF until it is removed for cleaning.

What is Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)?
The Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is an advanced active emissions control technology used in diesel engines. This system involves injecting diesel exhaust fluid (DEF), typically urea-based, into the exhaust prior to entering a special catalyst positioned in the exhaust downstream of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF).
The SCR catalyst, often similar in appearance to the DOC substrate, has a catalytic coating that interacts with the cleaned exhaust gas to significantly reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. If a malfunction in the diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) dosing system leads to crystallization of the fluid within the unit, SCRs can undergo cleaning procedures to restore optimal performance.
Understanding Diesel Emission Systems
Whether you are dealing with the Freightliner One Box or a Standard Diesel Emission System (DES) it is important to know the similarities and differences of all components as they are designed to work as a system.
See the table below for a quick guide to differentiating the systems.
Last but not least, check out this video from Cummins on aftertreatment: “How does an aftertreatment system work?”
Bonus: A Diesel Emissions Infographic
An overview of the aftertreatment system, showing the path of exhaust gas from the engine to the tailpipe.
From Engine
To Tailpipe
DOC
(Inlet)
DPF
SCR
(Outlet)
Sensor
Sensor
Sensor
Pressure
Pressure
Sensor
Sensor
Sensor
Redline Emissions Products is the industry leader in simplifying the diesel emission system. With our expertise and dedication to excellence, we ensure a seamless experience for our customers. Browse our website to learn more about our extensive range of aftertreatment products, equipment, and services.
For inquiries or more information on our aftertreatment parts, DFP Cleaning equipment, or how to become an authorized REP distributor, feel free to contact us. We are here to assist you and provide the support you need every step of the way.
Want to find out about becoming a Redline Emissions Products® dealer? We are happy to answer any questions you may have. Call 888-295-4670.
Need Tech Support or need help troubleshooting a DPF problem? No problem! Contact REP Support at 1-888-564-4209